A planned move to Belgium will be the beginning of a new life in one of the most dynamic and culturally diverse countries in Europe. Whether you want to find a job, study or unite your family, you need to prepare for every step of the process. Learn about the aspects of moving – obtaining a visa, residence permits, citizenship, finding a job, housing, social integration. This will help you become a full-fledged citizen of Belgian society.
Peculiarities of the country
Belgium is located in the western part of Europe, at the crossroads of European trade routes. It borders the Netherlands, Germany, France and Luxembourg, making it a convenient place to move and work. With its developed infrastructure, political stability and living standards, it is convenient for many immigrants.
Structure:
- The country consists of three regions: Flanders, Wallonia and Brussels. Each has its own cultural and linguistic identity: Flanders speaks Dutch, Wallonia speaks French, and Brussels speaks two languages.
- Government structures. The country is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. There are two levels of government: federal and regional. The most important institutions are the king, parliament and government.
- Nationalities living in Belgium. There are three main nationalities living in Belgium: the Flemish, the Walloons and the German-speaking Belgians. Despite the differences in language and Belgian culture, they maintain peaceful coexistence and cooperation.
- Currency: The euro (€) is used, making the country convenient for doing business with other European Union countries.
- Social structure. Belgian society has a high level of social security, a developed system of health care and social assistance. The principle of social solidarity operates here.
- Education and work. Good level of education, including free primary and secondary schools, as well as universities, institutes. The country’s labor market is an opportunity for workers in various fields, including IT, medicine and engineering.
The country continues to develop and open up new opportunities for immigrants, especially in the fields of technology, science and ecology. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in jobs in green and innovative industries. The country is also actively attracting investors and professionals, creating good conditions for businesses and startups.
Want to work in this country? Find out all the details on how to get a work visa to Belgium.
Interesting fact:
The country is the center of the European Union; the headquarters of NATO and the European Commission are located in Brussels, which makes the country an important political and economic player in Europe.
Pros and Cons of Belgium for Moving
It is a small but developed country located in the center of Europe. Neighboring France, Germany, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, it plays a role in the political and economic life of the European Union. The country has a developed economy, good social programs and a multicultural atmosphere. It has become a center for key European institutions, such as the European Parliament. But, like any country, it has advantages and disadvantages that are important to consider when deciding to move to Belgium.
Advantages of moving to Belgium:
- Multilingualism and cultural diversity. The country has 3 official languages: Dutch, French and German. This is useful for adaptation in a multicultural society.
- Quality of life. This is a state with a high standard of living – health care, education and social security.
- The infrastructure is developed. Convenient transport network (trains, buses, trams), which is convenient for moving around the country and beyond.
- Job Opportunities: With a developed economy, it offers jobs in a variety of industries – technology, medicine, finance and science.
- The center of the European Union. For those interested in a political career, work in international organizations is an advantage.
Moving to Belgium on your own also has its downsides, which will affect your choice of permanent residence and family reunification. Some aspects of life in this country may be unexpected for those who are not familiar with its peculiarities. It is necessary to analyze which downsides should be taken into account before making a decision.
Disadvantages of moving:
- High taxes in Belgium. Despite the high level of social services, the tax burden in Belgium will be too high for some immigrants.
- High cost of living: In large cities such as Brussels, the cost of renting a home in Belgium and daily expenses can be higher than average.
- Climate conditions: Rainy and grey climate will not suit migrants who prefer sunny and warm regions.
- Difficulties with Belgian bureaucracy. Paperwork and obtaining a visa for new immigrants can be complicated and lengthy.
- Language barrier: In some regions, knowledge of the local language is essential for integration.
According to 2024 statistics, the number of immigrants in Belgium continues to grow. The largest number of migrants came from neighboring countries such as France, Germany, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, as well as from Southern Europe, including Italy and Spain. The reasons for moving to Belgium are most often high wages, quality social programs and opportunities for professional growth, family reunification. But high taxes and climate conditions remain important factors influencing the choice of immigrants.
Fun fact:
Did you know that Belgium has the most cyclists in Europe?
Reasons for moving to Belgium
There are various factors that motivate people to move to Belgium. The country is attractive to professionals due to its high salaries, developed economy and many international organizations located in Brussels. It offers a healthcare and education system, making it a family-friendly place to live. It has stability, security and good living conditions, which are important for people looking for a reliable place to live, work and study.
Immigration for employment
One of the main reasons for moving to Belgium is employment. Depending on your citizenship, the process of labor immigration to the country differs. For EU citizens, moving and finding employment is usually easier, while residents of non-EU countries need to go through additional steps related to Belgian visas and work permits.
Stages of moving to Belgium for employment.
- Job search. It is necessary to find a vacancy that matches the profession and interests. For EU citizens it is possible to work without restrictions, for residents of other countries it is necessary to obtain a work permit.
- Applying for a visa/permit. For non-EU citizens, a work visa and work permit must be obtained. The process requires the submission of documents and proof of work qualifications.
- Preparation of documents. Collect the necessary documents: contract with the employer, diplomas, confirmation of work experience and financial solvency.
- Moving and registration. After moving to Belgium, you need to register at your place of residence, undergo a medical examination, take out health insurance and open a bank account.
- Obtaining permits and documents. If the work is for a long period, you need to obtain a residence permit and the necessary social documents, including insurance and pension contributions.
Most often, immigrants move to Brussels, Antwerp and Liege to work in Belgium. These cities are economic and business centers, where international companies and enterprises are concentrated. There is the most work here, and they are suitable for various professions.
You can learn all about the benefits and features of being a permanent resident of Belgium from this article.
Tip:
Belgium needs IT and engineering workers, as well as medical personnel.
Family reunion
The family reunification process allows immigrants in Belgium to bring their close relatives. The procedure is required for spouses, children, and in some cases parents or other dependent family members. The reunification process is necessary for the legal residence and work of family members, and for moving to Belgium for permanent residence.
Stages of family reunification:
- Where to apply. The process of family reunification in Belgium begins with the submission of an application to the local municipality or immigration center. You can contact the Federal Service for Foreigners (Office des étrangers):
- Address: R ue de la Loi 16, 1000 Brussels
- Website: office.fgov.be
- Phone: +32 2 793 80 00
- Documents. To submit an application, you must provide the following documents:
- Passport or identity card;
- Documents confirming family relationships (marriage certificates, birth certificates, etc.);
- Proof of financial solvency;
- Documents confirming your legal status in Belgium (e.g. work or study permit).
- Cost. Family reunification can cost between 100 and 150 euros, depending on the type of visa and additional services (for example, translation of documents or notary services).
- Waiting time. The process can take from several months to a year depending on the complexity of the case and availability of all documents. On average, the waiting time is 6-9 months.
Difficulties in the family reunification process include delays in processing applications and lack of documents. To avoid problems, you can prepare all the necessary papers in advance and ensure that the application deadlines are met. If the reunification is not completed, family members will not be able to legally reside and work in Belgium, which can lead to problems with the immigration authorities.
Important:
Belgium allows family reunification not only for citizens, but also for long-term residents, which allows relatives to arrive after several years of residence in the country.
Immigration for study
Belgium is an opportunity to study for EU citizens, students from countries outside the European Union. The high level of education, the availability of international programs and the choice of universities, colleges are convenient for foreign students. But for residents of countries outside the EU, the process of obtaining an education will be more difficult and will require additional documents and permits.
Stages of moving to Belgium to study:
- Choosing an institution. There are many universities and higher education institutions that offer educational programs. Students can choose courses in English, French and Dutch.
- Note: Universities such as Katholieke University Leuven, University catholic de Louvain and Vrije University Brussel is one of the most famous.
- For EU citizens. EU residents do not need a visa to study in Belgium. You will need proof of enrolment in an educational institution and proof of funds for living.
- For students from non-EU countries. To study in Belgium, students will need a Belgian study visa. Steps: submitting an application to the Belgian consulate or embassy, providing financial documents, proof of residence and health insurance.
- Health insurance and documents. All applicants, regardless of citizenship, must have health insurance for the entire period of stay in Belgium. Documents confirming the level of proficiency in the language in which the training will be conducted (for example, IELTS or TOEFL) are required.
Tuition fees for EU students may be lower than for residents from non-EU countries. Depending on the institution, the program costs between 900 and 4,000 euros per year. The cost of living for students is approximately 800-1,200 euros per month, including accommodation and food. You must prepare all the necessary documents in advance and have sufficient funds for living.
How does the integration of refugees in Belgium take place? Read the article for details of all processes.
Important:
For international students planning to study in Belgium, it is important to note that part-time work is permitted, but it should not exceed 20 hours per week during school hours.
Business immigration
Long-term relocation to Belgium is convenient for foreign entrepreneurs due to its strategic location in Europe, standard of living, favorable business climate. There are opportunities to create new companies, expand a business or open branches. Introduction to business immigration to Belgium requires understanding the local laws and the permit process, which makes the country accessible for creating successful commercial projects.
Stages of business immigration.
- Selecting the right visa. For business immigration to Belgium, you need to select the appropriate visa – for individual entrepreneurs, for setting up a company. There is also the possibility of obtaining a visa for startups.
- Address and website: Belgian consulates in the countries of residence. More information can be found on the official website of the Federal Migration Service of Belgium.
- Registering a business in Belgium. After receiving a visa, you must register a company. Belgian authorities offer various forms of business, including sole proprietorship and corporations. Where to apply: Belgian Chamber of Commerce (Handelsbeurs), local authorities. Address and telephone: Handelsbeurs, 1000 Brussels, tel.: +32 2 545 34 80. Website: www.chamber.be
- Preparation of documents. This includes proof of financial solvency, a business plan, and documentation of the company’s legal status. Health insurance and confirmation of education and qualifications in the relevant field are required.
- Applying for a visa. A business immigrant visa is issued through the Belgian consulate in the country of residence. The approximate waiting time is 2-3 months, depending on the complexity of the case.
- Obtaining a work permit. Once the company has been registered and the visa has been obtained, it is necessary to apply for a work permit if the plan is to work within the framework of the established business. This allows the entrepreneur to work in Belgium legally.
Business immigration to Belgium may encounter difficulties – bureaucratic procedures, requirements for financial documents. The process of registration, obtaining all permits may take longer than planned. But the country remains convenient for foreign entrepreneurs. The reasons are high standards of safety and infrastructure.
Important:
Belgium offers special tax incentives for start-ups and innovative companies, making it attractive for tech entrepreneurs.
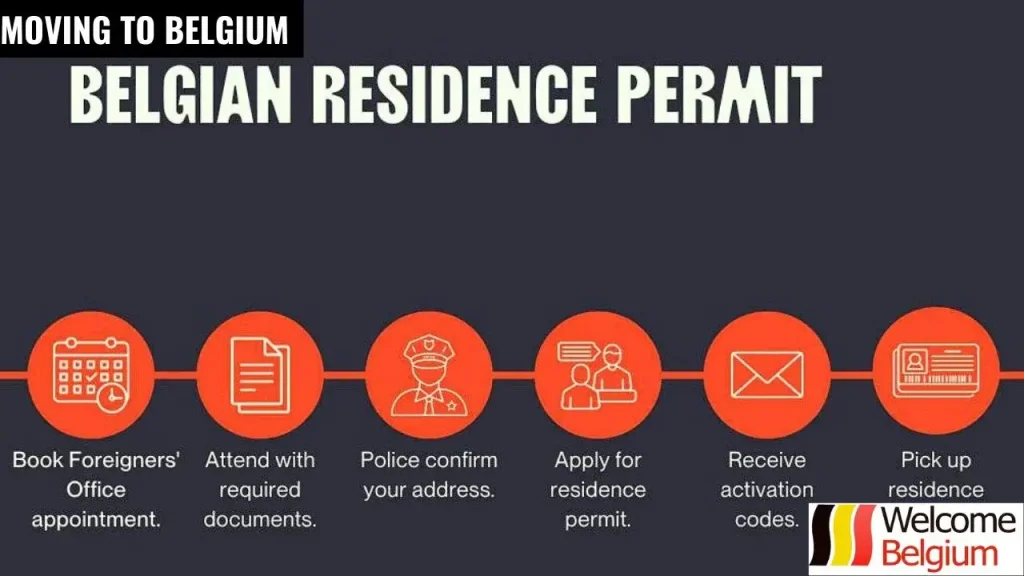
Obtaining a residence permit
Registration of a residence permit in Belgium after moving is necessary for immigrants. This allows you to legally stay in the country, opens access to various rights and opportunities – work, education and medical care. For EU citizens, the registration process is simpler, but for citizens of non-EU countries, there are additional requirements and stages. A residence permit in Belgium allows you to integrate into the country and become its resident.
Stages of obtaining permanent residence in Belgium:
- EU citizens. You do not need a residence permit to live in Belgium. However, for a long stay (more than 3 months) you must register with your local municipality. You must provide a passport, proof of financial solvency and a place to live.
- Residents of non-EU countries. You must contact the Belgian consulate in your country or the immigration authorities upon arrival. Requirements include filling out an application form, providing evidence of financial solvency, health insurance, diplomas and documents on work or study experience.
- Submission process. Collect all the required documents, the list depends on the type of visa (e.g. work, study or family visa). Then submit them to the consulate or local authorities in Belgium.
- Waiting and receiving a residence permit. Depending on the type of visa and region, the wait can take from 2 to 6 months. After receiving a residence permit, the immigrant gains access to social rights – health insurance, work.
- Temporary or permanent residence permit. After several years of residence in Belgium with a temporary residence permit, you can apply for permanent residence (PR).
If a residence permit is not issued, the immigrant risks facing administrative sanctions and possible deportation. In case of refusal to issue a residence permit, it is important to contact the migration service to find out the reasons and possible solutions. You can file an appeal or review the submitted documents.
Details about living in Belgium and what you need to do first are in our article.
Tip:
Once you have a residence permit in Belgium, you can also apply for citizenship if you live in the country for a certain number of years, usually 5 years.
Registration of citizenship
Obtaining Belgian citizenship is a step towards integration into the country. To become a citizen of the state, it is necessary to complete several stages and requirements – residence in the country for a set period of time. The process can take several years, depending on the circumstances and the type of visa.
Stages of obtaining citizenship.
- Residence for 5 years. The basic requirement for citizenship is legal residence in Belgium for at least 5 years (for EU citizens, 3 years). During this period, you must demonstrate that you have integrated into society, know the language, and comply with the laws.
- Applying for citizenship. You must apply for citizenship. The application is submitted to the local municipality where you live.
- Documents required to submit an application:
- Passport or other identification documents.
- Proof of residence in Belgium (rental agreements, bank statements, etc.).
- Documents confirming financial solvency.
- Proof of knowledge of one of the official languages of Belgium (French, Dutch or German).
- Certificate of completion of the integration test (for certain categories of applicants).
- Cost and waiting time. The application fee is 150-200 euros, depending on the type of application. The waiting time is 1-3 years, depending on the region and the complexity of the case.
- Review of the application and decision-making. Interview with local authorities, where documents will be checked. Decision on granting or denying citizenship.
- Obtaining citizenship. If the decision is positive, you will be invited to a citizenship ceremony, where the citizenship act will be signed and you will receive a Belgian passport.
Obtaining Belgian citizenship provides advantages – the right to work, the opportunity to participate in elections, as well as free movement within the EU. In case of refusal, clarify the reasons and, if necessary, file an appeal or re-apply with clarification of documents.
Important:
In Belgium, citizenship can be obtained not only through long-term residence, but also through marriage to a Belgian citizen, if you have been married for more than 5 years.
Moving and adaptation
After moving to Belgium, it is important to quickly adapt to the new living conditions. This includes getting to know the Belgian culture, understanding the peculiarities of the Belgian bureaucratic system and tax policy. The early adaptation stage also includes obtaining information about transport, social benefits and other important aspects of life.
What you need to do after moving:
- Register with the local municipality. After moving, you need to register your place of residence with the local municipality (commune). This will require a passport, proof of residence and sometimes health insurance.
- Setting up a bank account. For work and everyday needs, you will need a Belgian bank account. The process is quite simple, you will need to provide your passport and proof of address.
- Getting health insurance. In Belgium, health insurance is compulsory for all residents. You need to choose one of the private or public insurance companies and register.
- Getting to know the tax system. The Belgian tax system includes personal income tax, property taxes and VAT. You can understand the system by consulting with tax consultants or using government resources.
- Notifying your employer. If you have found a job, be sure to notify your employer of your arrival and the completion of all necessary documents.
- Knowledge of local languages. Belgium has three official languages: French, Dutch and German. Knowing at least one of these languages will be a plus for life and work.
Once all the bureaucratic stuff is sorted out, it’s time to learn about Belgium’s public transportation system, which includes trains, buses, and trams. It’s also important to learn about the social benefits and support available to residents, such as unemployment benefits and health care.